12 December 2013 – The United Nations human rights chief today voiced her disappointment at the re-criminalization of consensual same-sex relationships in India, calling it “a significant step backwards” for the country.
In a decision announced yesterday, the Supreme Court upheld a colonial-era law, Section 377 of the Indian Penal Code, which provides for the punishment of those found guilty of “unnatural offences.”
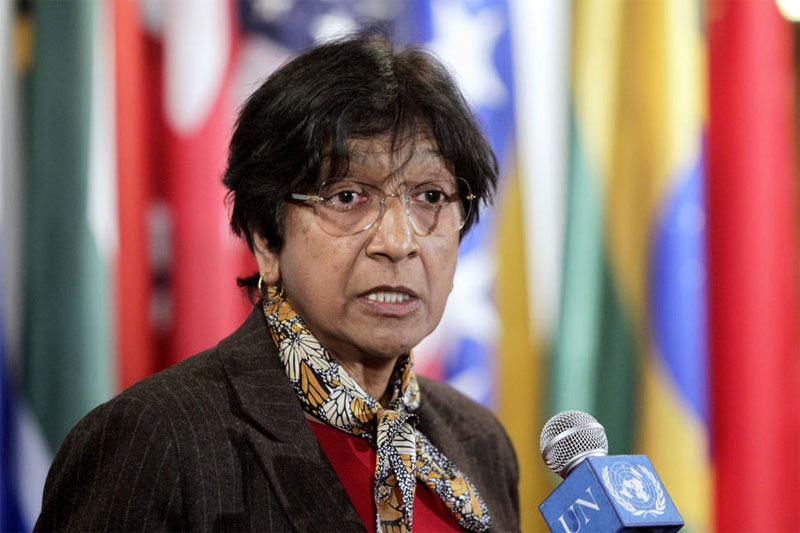
“Criminalising private, consensual same-sex sexual conduct violates the rights to privacy and to non-discrimination enshrined in the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, which India has ratified,” said UN High Commissioner for Human Rights Navi Pillay.
The Supreme Court’s decision, she added in a news release, represents “a significant step backwards for India and a blow for human rights.”
In 2009, the Delhi High Court struck down Section 377 in so far as it applied to sexual conduct between consenting adults in private, on the basis that criminalising such conduct is incompatible with the fundamental principles of equality, dignity and non-discrimination enshrined in the Indian Constitution. The matter was referred to the Supreme Court on appeal.
India’s top court yesterday declared Section 377 to be constitutionally valid, thereby overturning the 2009 High Court decision and re-instating the law.
“The Supreme Court of India has a long and proud history of defending and expanding protection of human rights. This decision is a regrettable departure from that tradition,” Ms. Pillay said.
She hoped that the Supreme Court might exercise its review procedure, in effect agreeing to rehear the case before a larger panel of judges, stating that such a review would provide an opportunity for judges to reconsider whether the decision took sufficient account of all relevant arguments.
More broadly, Ms. Pillay encouraged the Indian Parliament to take definitive action to decriminalise same-sex sexual conduct. She stressed the need to ensure effective protection for lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and intersex individuals from violence and discrimination.
The Joint UN Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) issued a statement in which it noted that the 2009 decision by the Delhi High Court to annul the law was widely considered “a milestone against homophobia and towards zero HIV-related discrimination.”
In the past four years since the law was annulled, there has been a more than 50 per cent increase in the number of sites providing HIV services for gay and other men who have sex with men, as well as transgender people in India.
“For the protection of public health and human rights, UNAIDS calls on India and all countries to repeal laws that criminalize adult consensual same sex sexual conduct. Such criminalization hampers HIV responses across the world.
“These laws not only violate human rights but also make it more difficult to deliver HIV prevention and treatment services to a population which is particularly affected by HIV.”
News Tracker: past stories on this issue
Countries must repeal laws that discriminate against LGBT individuals – UN officials